Comparison of Web Design: OOP vs. MVC
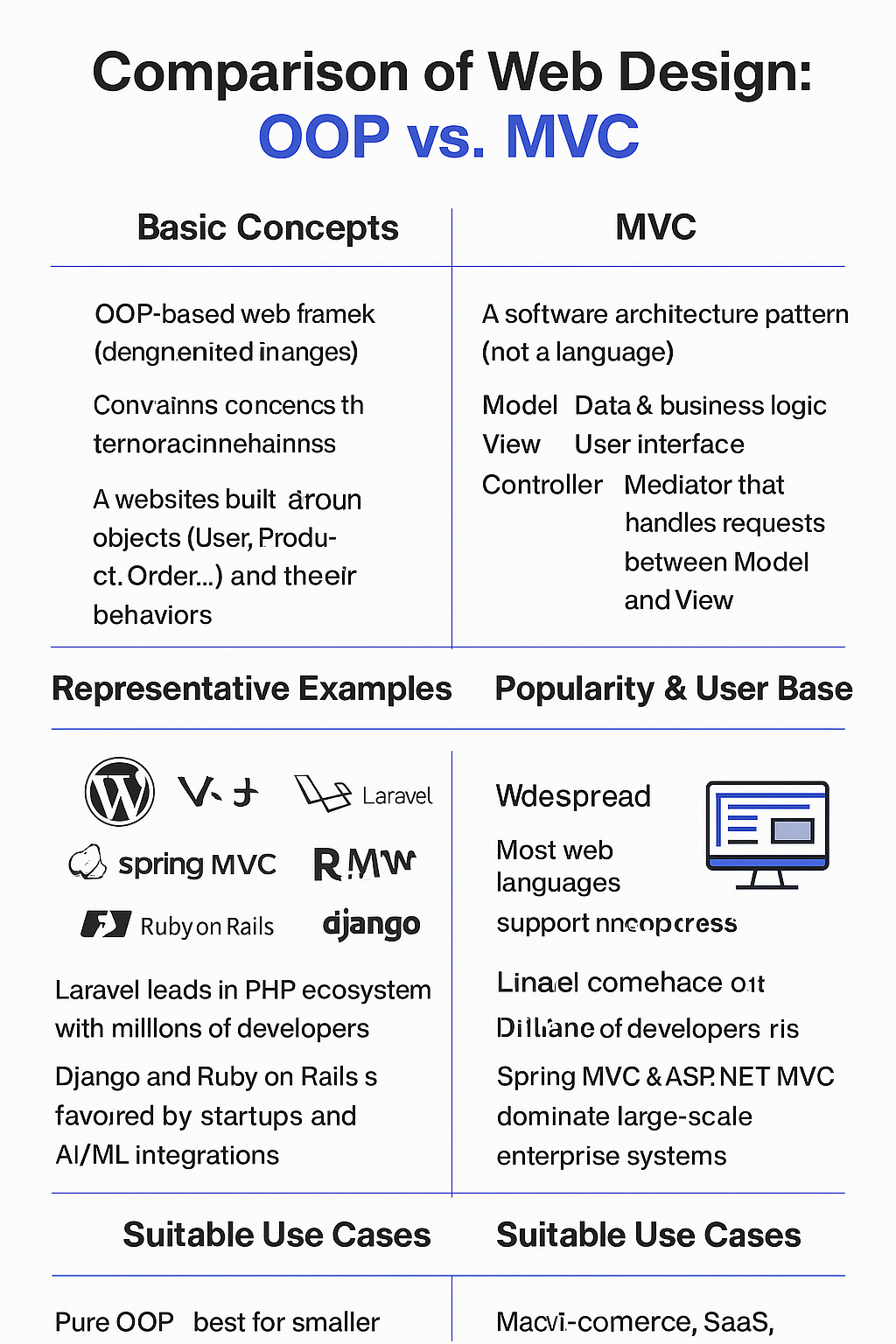
1. Basic Concepts
OOP (Object-Oriented Programming in Web Development)
- Essence: Organizes code into classes and objects, focusing on reusability, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
- Application in web: Commonly found in frameworks or object-oriented languages (Java, C#, PHP OOP, Python OOP).
- Approach to web design: A website is built around objects (User, Product, Order…) and their behaviors.
MVC (Model–View–Controller)
- Essence: A software architecture pattern (not a language). It separates concerns:
- Model: Data & business logic.
- View: User interface.
- Controller: Mediator that handles requests between Model & View.
- Application in web: Very popular in frameworks such as Laravel (PHP), Spring MVC (Java), ASP.NET MVC (C#), Ruby on Rails, Django (Python – a close variant called MTV).
2. Representative Examples
- OOP-based web frameworks / CMS:
- WordPress (PHP OOP, though not pure MVC).
- Joomla, Drupal.
- Custom applications built with Java or C#.
- MVC frameworks:
- Laravel (PHP) – currently the most popular in modern web development.
- Spring MVC (Java) – widely used for enterprise applications.
- ASP.NET MVC (C#) – within the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Ruby on Rails – popular among startups.
- Django (Python) – follows MTV, a variant of MVC.
3. Popularity & User Base
- OOP (general in web):
- Extremely widespread, since most web languages support OOP.
- WordPress powers ~43% of all websites globally (built on OOP concepts).
- MVC:
- Laravel leads in the PHP ecosystem, with millions of developers.
- Django and Ruby on Rails are highly favored by startups and AI/ML integrations.
- Spring MVC & ASP.NET MVC dominate in large-scale enterprise systems.
4. Suitable Use Cases
- Pure OOP:
- Best for smaller websites, CMS platforms, blogs, and business landing pages.
- Ideal for fast development with many plugins available.
- MVC:
- Suited for e-commerce, SaaS, fintech, ERP, and CRM systems.
- Perfect when clear architecture, long-term maintenance, and scalability are required.
5. Expert Opinions on the Future
- Competition:
- MVC will remain the standard for modern web applications, especially in microservices & cloud-based systems.
- Pure OOP will continue to thrive due to CMS platforms (WordPress, Joomla).
- Security:
- MVC frameworks generally offer stronger built-in security (CSRF tokens, XSS filtering, ORM against SQL Injection).
- Pure OOP can be less secure if developers don’t strictly follow best practices.
- Development speed:
- MVC is faster for large teams (tasks are clearly divided: backend → Model, frontend → View, fullstack → Controller).
- OOP is faster for individuals or small teams working on simpler sites.
- Future trends:
- MVC combined with OOP will remain the dominant approach (e.g., Laravel, Django are both OOP and MVC).
- Newer patterns such as MVVM (Angular, Vue, React + backend APIs) and Serverless architecture are rising fast.
- Still, MVC is considered the “backbone” of most large-scale web systems.
✅ Summary:
Future: MVC will remain central but will increasingly combine with API-first development, SPA frameworks (React, Vue, Angular), and microservices.
For smaller websites, personal projects, CMS → OOP (WordPress, Joomla) is more practical.
For modern, scalable web applications with many users → MVC frameworks (Laravel, Django, Spring MVC) are the optimal choice.