Applying AI in Agriculture: The Future of Global Agriculture

The growing global population, expected to reach 10 billion by 2050, is putting significant pressure on the agricultural sector to increase crop production and maximize productivity. To address the emerging food shortage, two potential approaches have emerged: expanding land use and adopting large-scale farming, or adopting improved methods and leveraging technological advances to increase productivity on existing farmland
Driven by numerous obstacles to achieving desired crop yields on limited land, labor shortages, climate change, environmental concerns, and declining soil fertility, to name a few, the modern agricultural landscape is evolving, expanding in many different innovative directions. Agriculture has certainly come a long way since the days of the hand plow or horse-drawn tractor. Each season brings new technologies designed to improve efficiency and maximize harvests. However, both individual farmers and global agribusinesses often miss out on the opportunities that AI in agriculture can bring to their farming practices.
At Intellias, we have been working with the agriculture industry for over 20 years, successfully implementing practical technology solutions. Our focus is on developing innovative systems for quality control, traceability, compliance practices, and more. Now, let’s dive deeper into how new technologies can help your agribusiness move forward.
Benefits of AI in Agriculture
Until recently, using the words AI and agriculture in the same sentence may have seemed like an odd combination. After all, agriculture has been the backbone of human civilization for millennia, providing food and contributing to economic development, while even the most primitive AI emerged only a few decades ago. However, innovative ideas are being introduced into every industry, and agriculture is no exception. In recent years, the world has witnessed rapid advances in agricultural technology, revolutionizing farming practices. These innovations are becoming increasingly necessary as global challenges such as climate change, population growth, and resource scarcity threaten the sustainability of our food system. The introduction of AI addresses many of these challenges and helps mitigate many of the drawbacks of traditional agriculture.
Data-Driven Decisions
The modern world is all about data. Organizations in the agricultural sector use data to gain detailed insights into every detail of the farming process, from understanding each acre of a field to tracking the entire supply chain of produce to gaining insight into the processes that drive yield. Predictive analytics powered by AI has made its way into the agricultural business. Farmers can collect and then process more data in less time with AI. Additionally, AI can analyze market demand, forecast prices, and determine the optimal time to plant and harvest.
Artificial intelligence in agriculture can help explore soil health to gather insights, monitor weather conditions, and recommend fertilizer and pesticide use. Farm management software boosts production along with profitability, allowing farmers to make better decisions at every stage of the crop growing process.
Cost Savings
Improving farm productivity is a constant goal for farmers. Combined with AI, precision agriculture can help farmers grow more crops with fewer resources. AI in agriculture combines best practices in soil management, variable rate technology, and the most effective data management methods to maximize yields while minimizing costs.
AI applications in agriculture provide farmers with real-time crop insights, helping them determine which areas need irrigation, fertilization, or pesticide treatment. Innovative farming methods like vertical farming can also increase food production while minimizing resource use. The result is reduced herbicide use, better harvest quality, higher profits, and significant cost savings.
The impact of automation
Farming is hard work, so labor shortages are nothing new. Fortunately, automation offers a solution that doesn’t require hiring more people. While mechanization has transformed agricultural activities that required sweat and animal labor into tasks that take only a few hours, a new wave of digital automation is revolutionizing the sector once again.
Automated agricultural machinery such as driverless tractors, smart irrigation systems, fertilization systems, IoT-powered agricultural drones, smart sprayers, vertical farming software, and AI-powered greenhouse robots for harvesting are just a few examples. Compared to any farm worker, AI-controlled tools are much more efficient and precise.
Detecting Leaks or Damage to Irrigation Systems
AI plays a key role in detecting leaks in irrigation systems. By analyzing data, algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies that indicate potential leaks. Machine learning (ML) models can be trained to recognize specific signs of leaks, such as changes in water flow or pressure. Real-time monitoring and analysis allows for early detection, preventing water waste and potential crop damage.
AI also combines weather data with crop water needs to identify areas that are using too much water. By automatically detecting leaks and providing alerts, AI technology improves water efficiency, helping farmers save resources.
Monitoring Crops and Soil
The wrong combination of nutrients in the soil can severely impact crop health and growth. Identifying these nutrients and determining their impact on crop yields with AI allows farmers to easily make the necessary adjustments.
While human observation is limited in accuracy, computer vision models can monitor soil conditions to collect the precise data needed to combat crop diseases. This plant science data is then used to determine crop health, predicting yields while flagging any specific problems. Crops trigger AI systems through sensors that detect their growing conditions, triggering automatic adjustments to the environment.
In fact, AI in agriculture and livestock can accurately monitor the growth stages of wheat and the ripening of tomatoes with a speed and accuracy that no human can match.
Disease and Pest Detection
In addition to detecting soil quality and crop growth, computer vision can detect the presence of pests. This works by using AI in agricultural projects to scan images for mold, rot, insects, or other threats to crop health. Combined with alert systems, this helps farmers act quickly to kill pests or isolate crops to prevent the spread of disease.
AI technology in agriculture has been used to detect apple black rot with over 90% accuracy. It can also identify insects such as flies, bees, moths, and more with the same accuracy. However, researchers first need to collect images of these insects to have the necessary training dataset size to train the algorithm.
Monitoring Livestock Health
It may seem easier to detect health problems in livestock than in crops, but in reality, it is extremely difficult. Thankfully, AI for agriculture can help with this. For example, a company called CattleEye has developed a solution that uses drones, cameras, and computer vision to remotely monitor livestock health. The solution detects abnormal livestock behavior and identifies activities such as birthing.
CattleEye uses AI and ML solutions to determine the impact of diet and environmental conditions on livestock and provide valuable insights. This knowledge can help farmers improve the health of their livestock to increase milk production.
Smart Pesticide Application
Farmers are now well aware that pesticide application is ripe for optimization. Unfortunately, both manual and automated application processes have significant limitations. Manual pesticide application increases precision when targeting specific areas, although it can be slow and difficult. Automatic pesticide spraying is faster and less labor intensive, but often lacks precision, leading to environmental pollution.
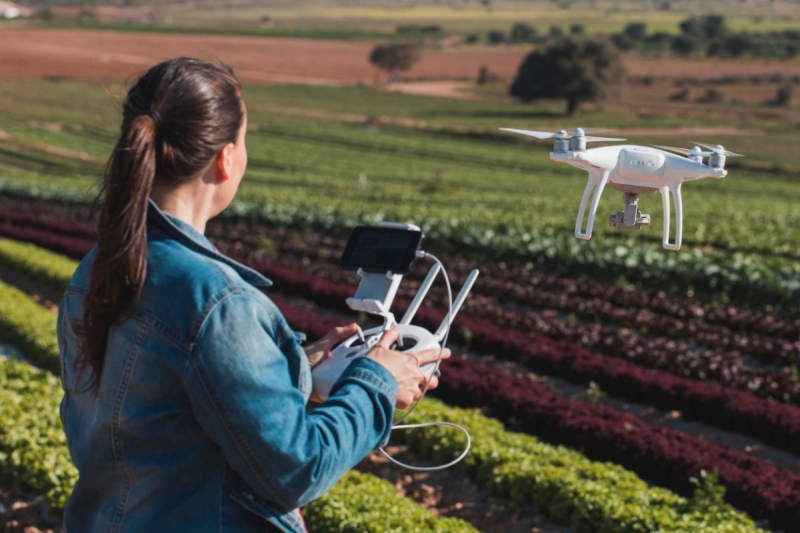
AI-powered drones offer the best advantages of each method while avoiding their drawbacks. Drones use computer vision to determine how much pesticide to spray in each area. While still in its infancy, the technology is rapidly becoming more accurate.
Yield Mapping and Predictive Analytics
Yield mapping uses ML algorithms to analyze large data sets in real time. This helps farmers understand crop patterns and characteristics, allowing for better planning. By combining techniques such as 3D mapping, sensor data, and drones, farmers can predict land productivity for specific crops. Data is collected over multiple drone flights, allowing for increasingly accurate analysis using algorithms.
These methods allow for accurate predictions of future yields for specific crops, helping farmers know where and when to sow seeds and how to allocate resources for the best return on investment.
Automated weeding and harvesting
Similar to how computer vision can detect pests, it can also be used to detect weeds and invasive plants. When combined with machine learning, computer vision analyzes the size, shape, and color of leaves to distinguish weeds from crops. Such solutions can be used to program robots to perform robotic process automation (RPA) tasks, such as automated weeding. In fact, such a robot is already being used effectively. As these technologies become more accessible, both weeding and harvesting crops could be done entirely by intelligent robots.
Harvested Produce Sorting
AI is not only useful in identifying potential problems with crops while they are growing. It also plays a role after the produce has been harvested. Most sorting processes are traditionally done manually, however AI can classify produce more accurately.
Computer vision can detect pests and diseases in harvested crops. What’s more, it can sort produce based on shape, size, and color. This allows farmers to quickly sort produce into categories—for example, to sell to different customers at different prices. By comparison, traditional manual sorting methods can be labor-intensive.
Surveillance
Security is an important part of farm management. Farms are frequent targets for thieves, as it’s difficult for farmers to monitor their fields around the clock. Animals are another threat—whether it’s a fox breaking into a chicken coop or a farmer’s own livestock damaging crops or equipment. When combined with video surveillance systems, computer vision and ML can quickly identify security breaches. Some systems are even advanced enough to distinguish employees from unauthorized visitors.
According to intellias.